As businesses grow increasingly reliant on data-driven decision-making, the debate between edge computing and cloud computing continues to heat up. Both these technologies present unique advantages and benefits that may lead to the operational success of any business. The ultimate question still remains: which of the two computing solutions better suits the future? More importantly, how can businesses make the most of these advancements?
In this blog, we will explore the key differences between edge computing and cloud computing, their strengths, and how businesses can embrace these technologies to build smarter, faster, and more efficient IT infrastructures.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing has changed the way modern information technology works. Organizations can keep, process, and manage data in central data centers, accessing it over the internet. By leveraging cloud management services from providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, businesses can efficiently expand their operations without significant upfront investment in hardware.
Advantages of Cloud Computing:
- Scalability: Cloud platforms enable businesses to adjust resources whenever required, ideal for growing businesses or those whose workloads fluctuate.
- Accessibility: The cloud allows one to access data anywhere in the world, hence convenient for remote working.
- Cost Efficiency: It eliminates the excess costs of infrastructure through its pay-as-you-go system.
- Innovation Ready: The tools for artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analysis that come with the cloud platforms enhance innovation.
What is Edge Computing?
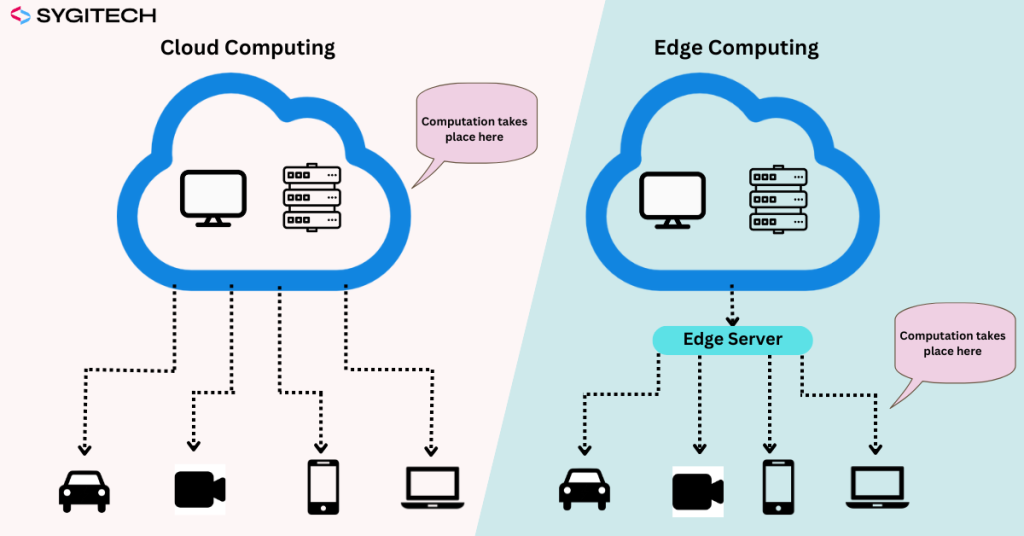
Edge computing is the new way of doing computing where data is processed near the source- like IoT devices, sensors, or local servers rather than big central data centers. This technique reduces delay and helps make decision-making faster, especially for things that need answers quickly, like autonomous vehicles or industrial automation. Many experts view edge computing as the future of cloud computing, offering innovative solutions for real-time data processing and localized operations.
Advantages of Edge Computing:
- Real-time data processing: By cutting down the time taken for data to travel, edge computing makes response times faster.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: The system sends only the necessary data to the cloud, saving bandwidth and lowering costs.
- Localized Security: Organizations can handle sensitive data locally, reducing the risks associated with sending it over networks.
- IoT Enablement: Edge computing is essential for IoT, allowing devices to work on their own and communicate easily.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Key Differences
| Features | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
| What it is | It’s when data is processed and stored in huge remote data centers that you access via the internet. | Data is processed right where it’s generated-on devices or nearby nodes-before it’s sent to the cloud. |
| Data Processing | Processes data in large data centers or centralized cloud servers. | Processes data locally on devices or at edge nodes before sending it to the cloud. |
| Latency | Higher latency due to the distance between the user/device and the cloud server. | Lower latency as data is processed closer to the source. |
| Bandwidth usage | Requires significant bandwidth for transmitting large volumes of data to the cloud. | Reduces bandwidth usage by processing data locally and sending only necessary information to the cloud. |
| Scalability | Super easy to scale-cloud providers have plenty of resources to grow with your needs. | It’s more limited-edge devices can handle only so much before you need more local nodes or devices. |
| Data Security | While cloud security is strong, data being stored far away might raise privacy concerns if not handled right. | Data stays close to home, offering more privacy, but securing lots of devices and nodes can get tricky. |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs but can add up with storage and processing fees over time. | Higher upfront costs for local devices, but ongoing costs are often lower because less data needs to travel. |
| Real time processing | Not the best for real-time tasks—delays can happen as data travels to and from the cloud. | Ideal for real-time action, as the data is processed immediately where it’s created. |
| Reliability | Depends on the internet connection—if it’s down, you can lose access to services. | More reliable for certain tasks because if the internet fails, local processing keeps things going. |
When to Use Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
Both technologies have unique functions, and the decision between them often hinges on particular business needs:
Use Cloud Computing If:
- You require scalable storage for extensive datasets.
- Your applications do not demand ultra-low latency.
- Accessibility and flexibility are key priorities for your business.
Use Edge Computing If:
- Real-time processing is essential, as in healthcare or autonomous vehicles.
- You need to reduce bandwidth usage.
- You are deploying IoT systems where devices must communicate locally.
Consider a Hybrid Model:
For many businesses, the best approach is a combination of both. By leveraging managed cloud services alongside edge computing, you can benefit from the scalability of the cloud while enjoying the speed and efficiency of edge processing.
Challenges in Decentralized Data Management
Decentralized data management, which combines edge and cloud computing, brings notable benefits but also several challenges. Data security is a primary concern; edge computing processes and stores sensitive information closer to its source, which can increase the risk of unauthorized access or breaches. In contrast, cloud computing focuses on securing data during transit, which comes with its own set of vulnerabilities.
Another challenge is managing costs; while edge computing can lower bandwidth expenses by processing data locally, the initial investment in local edge devices can be high. Conversely, cloud usage can escalate costs if businesses don’t closely monitor and optimize resource consumption.
Additionally, creating a seamless hybrid model that integrates edge and cloud computing requires careful planning and specialized knowledge to ensure smooth interoperability and prevent operational inefficiencies.
The Future of Decentralized Data
The future combines the strengths of both edge and cloud computing. As AI, 5G, and IoT evolve, businesses will adopt hybrid models for maximum benefit.
- Healthcare: Edge computing processes real-time data, while the cloud stores patient records.
- Smart Cities: Edge devices manage traffic, and the cloud supports urban planning.
- Retail: Edge computing offers personalized in-store recommendations, while the cloud handles inventory and supply chains.
Conclusion
Edge computing and cloud computing are complementary technologies shaping the future of decentralized data. By understanding their strengths and limitations, businesses can implement solutions that drive innovation, efficiency, and scalability.